Introduction to Avantium and PEF
Avantium is a pioneering technology company focused on advancing renewable chemistry. Their mission is to facilitate the transition towards a fossil-free future by developing sustainable materials derived from renewable carbon sources. PEF, produced from plant-based sugars, is one such material that offers promising alternatives to conventional plastics like polyethylene terephthalate (PET).
The production of PEF begins with the conversion of first-generation feedstocks, specifically sugars extracted from crops like wheat. These sugars are transformed into 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA), the core building block of PEF. This process not only helps in reducing greenhouse gas emissions but also contributes to a circular economy by enabling recycling.
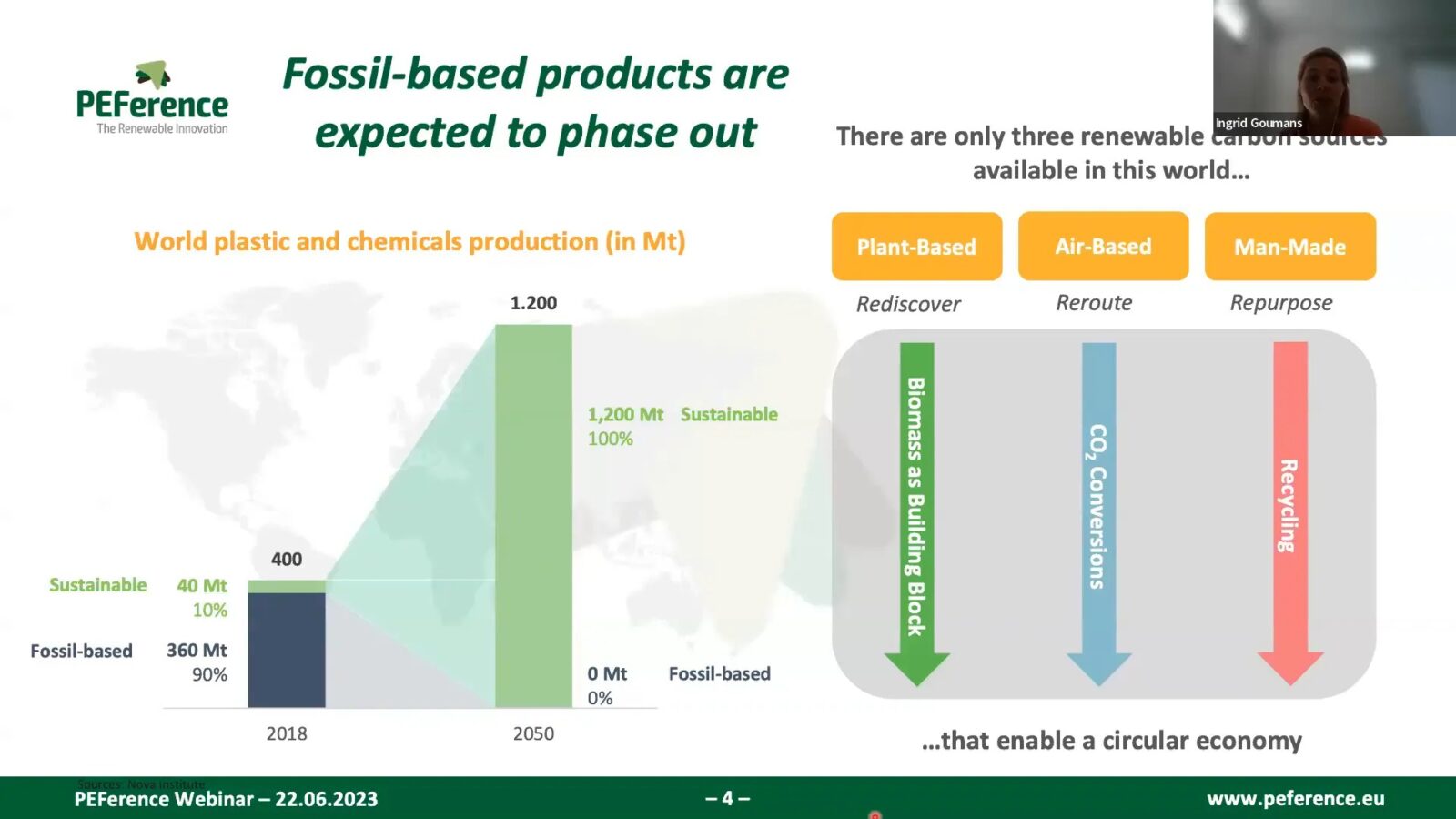
Understanding the Production Process
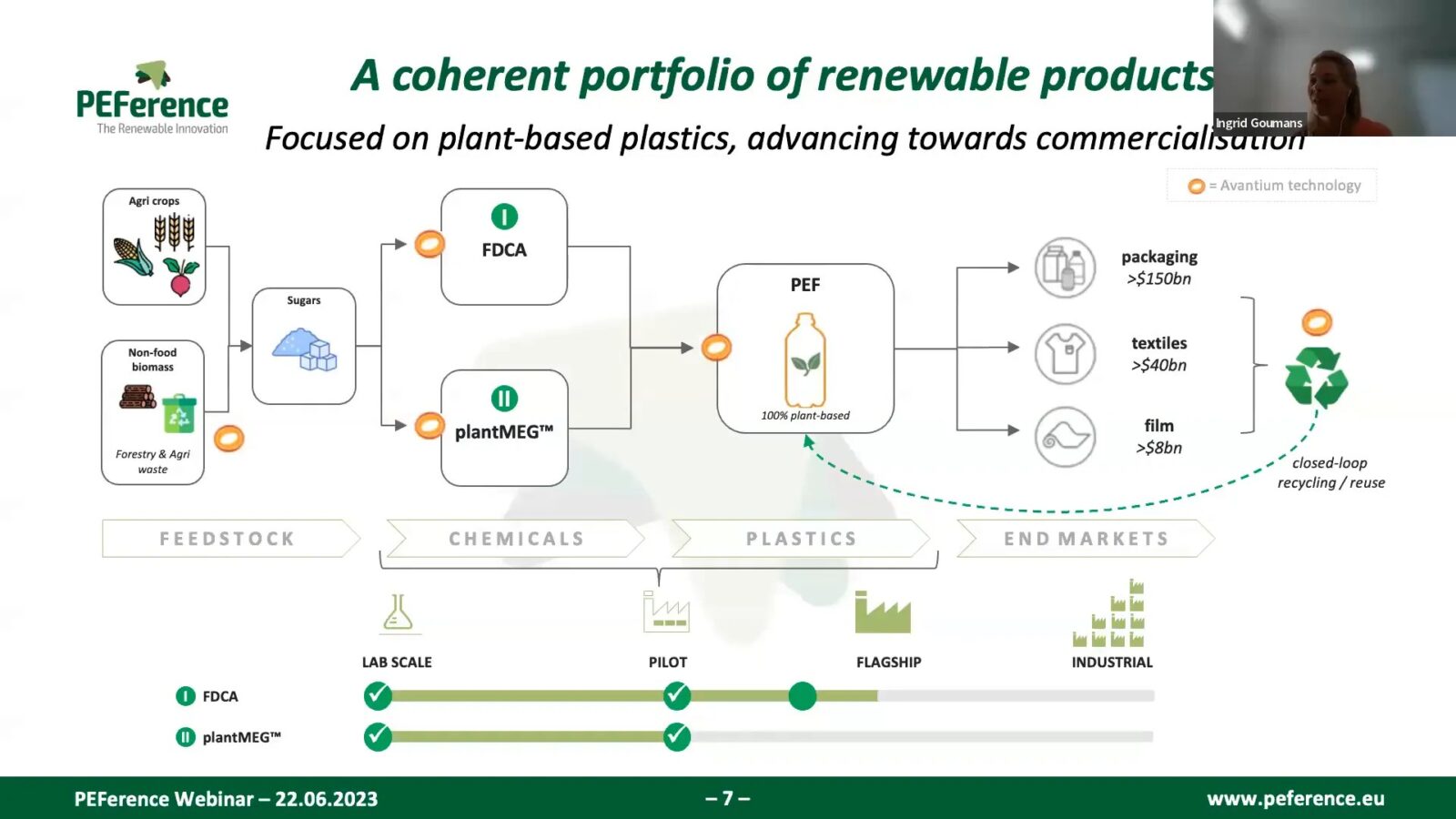
The production of PEF involves multiple stages, starting from the sourcing of plant-based feedstocks to the polymerization of FDCA with monoethylene glycol (MEG). While the current technology primarily utilizes first-generation feedstocks, there’s potential for incorporating second-generation feedstocks in the future.
PEF is engineered to have superior properties compared to PET, including enhanced barrier characteristics, which allow for longer shelf lives of products packaged in PEF. Additionally, PEF can be processed using the same equipment as PET, making the transition smoother for manufacturers.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of PEF Bottles
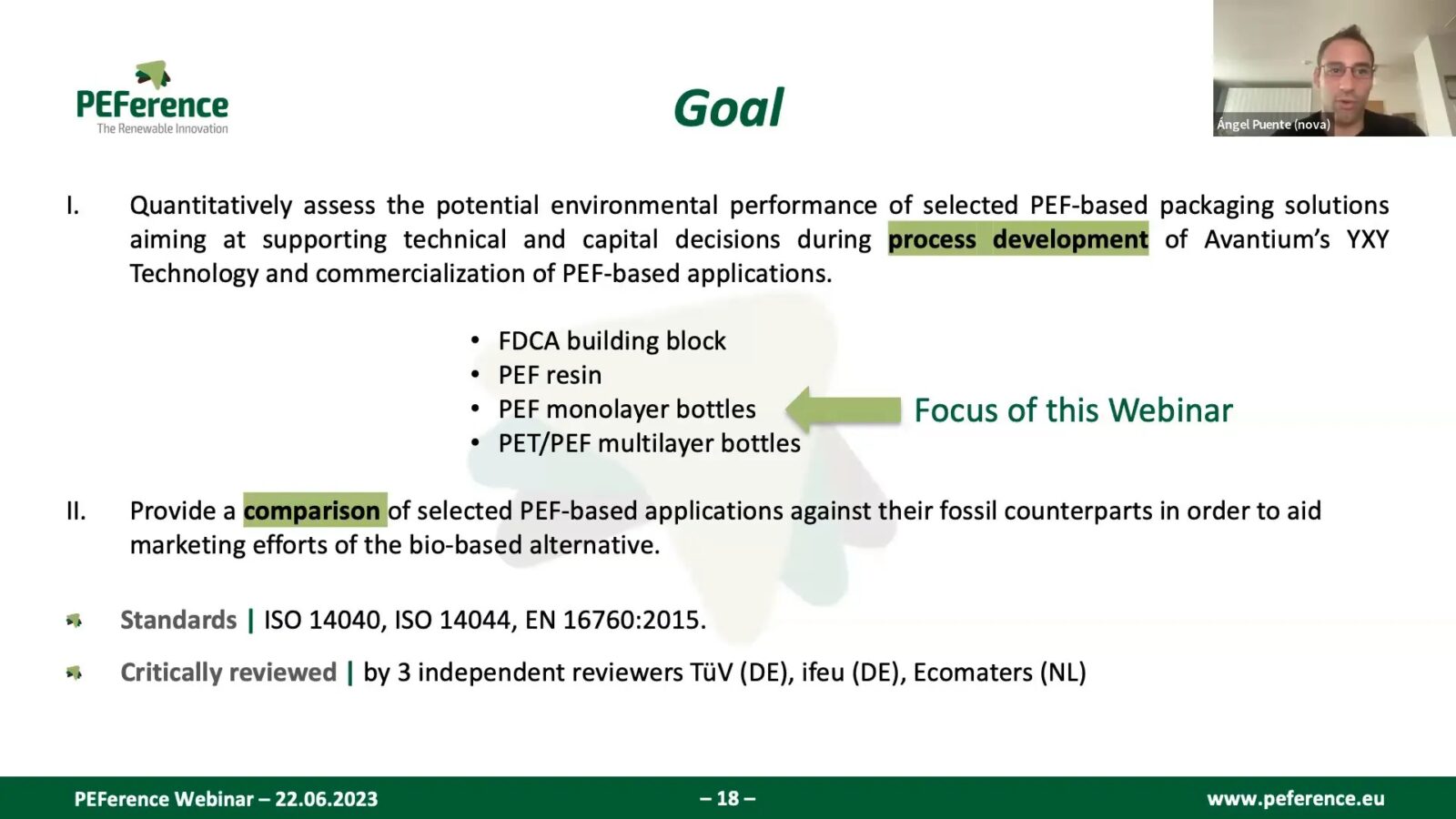
The LCA of PEF bottles is crucial in understanding their environmental impact throughout their life cycle. The assessment evaluates various stages, from the extraction of raw materials to production, use, and end-of-life scenarios. The goal of the LCA is to quantitatively assess the environmental performance of PEF compared to traditional PET bottles.
Conducted under ISO standards, the LCA considers multiple impact categories, including greenhouse gas emissions, resource depletion, and effects on human health and the environment. This comprehensive approach provides valuable insights into the sustainability of PEF bottles.
Key Findings from the LCA
The LCA reveals that PEF bottles can lead to a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions—approximately 61% less over their life cycle compared to PET bottles. This is a substantial finding, especially considering the established market presence of PET.
Moreover, PEF demonstrates a 34% reduction in the use of fossil resources. The primary contributors to these environmental benefits are the renewable carbon sources utilized in its production, which sequester carbon dioxide during the growth phase of the plants used as feedstock.
Environmental Benefits of PEF
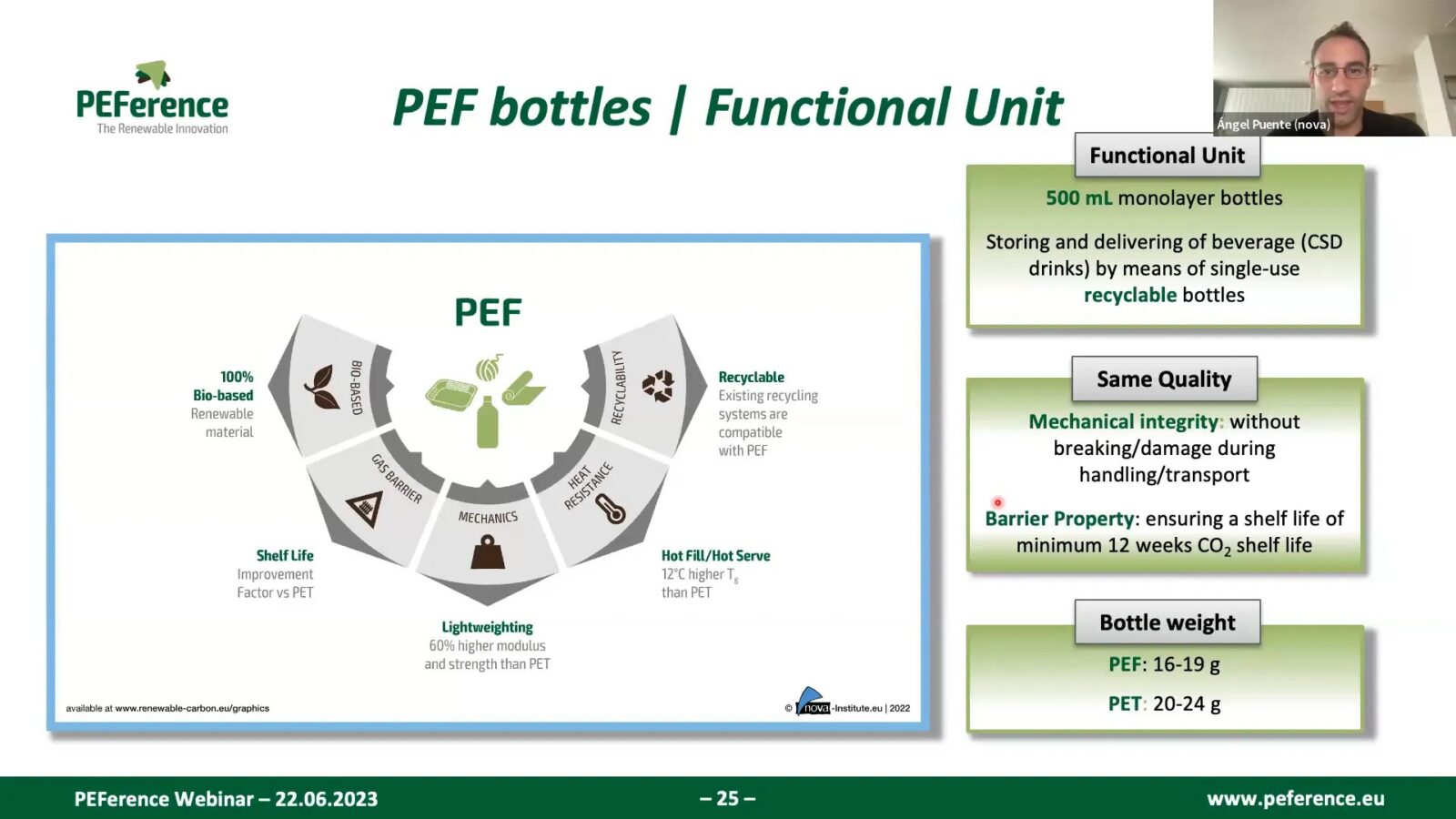
One of the standout features of PEF is its ability to maintain high performance while being environmentally friendly. The material boasts superior barrier properties, which means it can keep carbonated beverages fresh for extended periods without requiring excessive material usage.
- Superior Barrier Properties: PEF has a ten times better oxygen barrier than PET, which is crucial for preserving the quality of sensitive products.
- Recyclability: PEF is fully recyclable and can be integrated into existing PET recycling streams, ensuring a circular lifecycle.
- Reduced Material Use: The improved mechanical properties of PEF allow for lightweight packaging solutions, minimizing resource consumption.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its many advantages, PEF is still in the early stages of commercialization. The current production scale is limited, with ongoing efforts to scale up to industrial levels. Avantium is constructing a flagship plant capable of producing 5 kilotons of PEF per year, with plans for further expansion.
Future developments aim to incorporate second-generation feedstocks, which could further enhance the sustainability of PEF production. Additionally, ongoing research will explore other applications of PEF beyond packaging, potentially expanding its market reach.
Conclusion
The journey of PEF from plant-based sugars to a fully recyclable polymer represents a significant step towards sustainable materials in the packaging industry. The findings from the LCA highlight the environmental benefits of PEF, making it a viable alternative to traditional fossil-based plastics.
As Avantium continues to innovate and scale its production, the potential for PEF to contribute to a circular economy becomes increasingly promising. The transition to renewable carbon sources is not just beneficial for the environment; it also aligns with the growing consumer demand for sustainable products.
For more information on the PEFerence project and its initiatives, visit PEFerence – The Renewable Innovation.